PSY3309
Behavioral Neuroscience


Dr. Smith
Florida Southern College
Cerebellum
Disclaimer: All structures that have been covered in the lab manual so far can be tagged on a test. This webpage covers the majority of the structures that can be tagged on this view, however, please note that there may be other structures not listed here that can be tagged on the cerebellum.

Anterior Lobe
On this view the entire anterior lobe can be seen directly ventral to the superior colliculi. It is also surrounded by the posterior lobe and the corpus cerebelli.
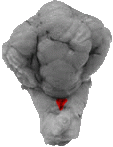
Area Postrema
If one were to separate the medulla and spinal cord from the cerebellum (in this caudal view), one can see the area postrema, which is the depression between the "Y" shaped portion of the hindbrain.

Basis Pedunculi
The basis pedunculi marks the most ventral portion of the midbrain.
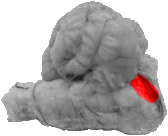
Brachium Pontis
On a side view of the cerebellum the brachium pontis is an extension of the pons that projects dorsally into the cerebellum.
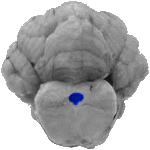
Cerebral Aqueduct
In this front view of the cerebellum, the hole in the midbrain (at the level of the tectum), is the cerebral aqueduct.

Corpus Cerebelli
The corpus cerebelli, or cerebellar hemispheres, are the predominant lateral portions of the cerebellum, and they can be seen on all three cerebellum views.
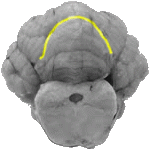
Fissura Prima
The fissura prima is a horseshoe shaped line that separates the anterior lobe from the subsequent posterior lobe.

Flocculus
The flocculus can be seen on both the front and side views of the cerebellum. The flocculus can be seen as the most ventro-lateral portion of the cerebellum, falling directly below the corpus cerebelli. On the side view the flocculus is also dorsal to the brachium pontis, trigeminal nerve, and the trapezoid body.

Fourth Ventricle
From the back view the "Y" shaped hindbrain also gives way to a space that is directly beneath the cerebellum. This is the caudal portion of the fourth ventricle, and its contents flow directly into the central canal of the spinal cord.
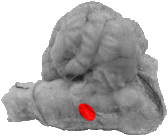
Olive
On a side view of the cerebellum the olive falls inside the intersection of the trapezoid body and the pyramid.

Pons
The pons, on the lateral view of the cerebellum, can be noted as a large ventral mass that falls directly below the brachium pontis, the trigeminal nerve.

Posterior Lobe
The posterior lobe can be seen on all three cerebellum views. On the front view its dorsal (and actually caudal) to the anterior lobe and fissura prima. On this view it is also medial to the corpus cerebelli on each side of the cut. On a side view it can be seen as the dorsal most portion of the cerebellum that wraps over the corpus cerebelli. On the back view is it dorsal to the hindbrain and is again medial to the corpus cerebelli.

Pyramid
The pyramid marks the most ventral portion of the medulla and it can be seen running directly between the trapezoid body and the spinal cord.

Spinal Cord
The spinal cord marks the very end of the cerebellum section both on a side and back view.

Inferior Colliculus
On this front section please note that the dorsal (bumps) are not touching each other. Those bumps at the top of the midbrain represent the inferior colliculus. If there were two large rounded masses that appeared to be touching each other (with only a line of separation between them), then the highlighted structures would in fact be the superior colliculus.

Tectum
The tectum is all matter that is dorsal and lateral to the cerebral aqueduct.

Tegmentum
The tegmentum is the entire top half of the cerebral peduncle and is an area located directly below the tectum and cerebral aqueduct.
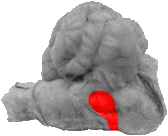
Trapezoid Body
The trapezoid body is a rectangular region located directly behind the pons and trigeminal nerve.

Trigeminal Nerve
The trigeminal nerve can be clearly seen on the side view of the cerebellum. It often times looks like a (bump) between the brachium pontis and the trapezoid body.