PSY3309
Behavioral Neuroscience


Dr. Smith
Florida Southern College
Dorsal View
Disclaimer: All structures that have been covered in the lab manual so far can be tagged on a test. This webpage covers the majority of the structures that can be tagged on this view, however, please note that there may be other structures not listed here that can be tagged on the dorsal view.
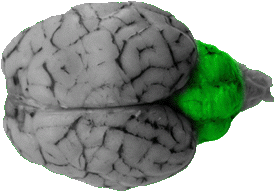
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a large structure that can be seen covering the hindbrain on this view.
Corpus Cerebelli
The corpus cerebelli (or cerebellar hemispheres) are the large, lateral bodies of the mid-line of the cerebellum (i.e., the vermis).
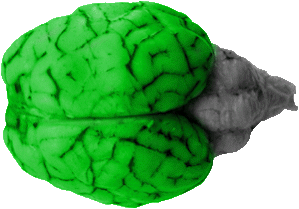
Cortex
The cerebral cortex is the large series of gyri that comprise most of the dorsal view. This general structure is sub-divided into five major lobes(frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal and insular), and these lobes (as well as individual gyri) are distinguished by lines called sulci and fissures.
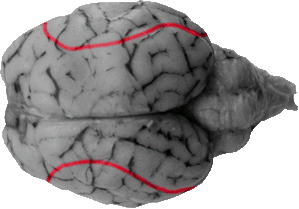
Cruciate Fissure
The cruciate fissure is a line that runs laterally from the longitudinal fissure, and it separates the rostral one third of the cortex (the frontal lobe) from the caudal two thirds of the cortex. In doing so it forms a cross, or crucifix with the longitudinal fissure (which is how it gets its name). It is analogous to the central sulcus in the human brain.

Diagonal Sulcus
The diagonal sulcus runs laterally from roughly an inch rostral to the cruciate fissure. This line generally separates gyri within the frontal lobe.

Ectolateral Gyrus
Lies even more lateral than the entolateral sulcus. It is separated from the entolateral sulcus by the lateral sulcus.

Entolateral Gyrus
Located in the most caudal region of the occipital lobe, it is visible just lateral to the back of the longitudinal fissure. It is considered by many to be the primary visual cortex.
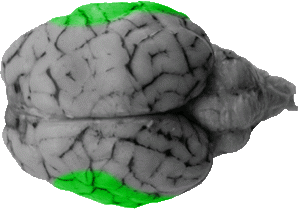
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is comprised of approximately one third of the cerebral cortex from the dorsal view.Its caudal boundary is marked by the cruciate fissure, which separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe in the sheep brain. In a human brain the frontal lobe extends much further back to a boundary called the central sulcus.The primary function of the frontal lobe is for voluntary movement, but its activity has been highly correlated with higher intellectual behaviors.
Lateral Gyrus
The entolateral gyrus is medial to the lateral gyrus.

Lateral Sulcus
The lateral sulcus separates the ectolateral gyrus from the lateral gyrus.
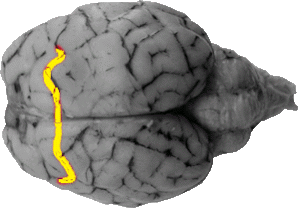
Longitudinal Fissure
The longitudinal fissure separates the left and right cerebral cortex hemispheres. It runs from a rostral to caudal direction along the entire mid line of the cerebral cortex.
Medial Frontal Gyrus
The medial frontal gryus is the gyrus that runs with the superior frontal gyrus but is lateral to the superior frontal sulcus.
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is the caudal portion of the cerebral cortex. Its primary function is to process vision.
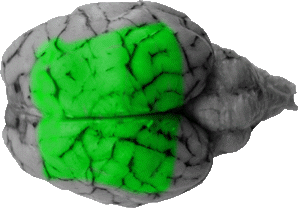
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe consists of all gyri between the frontal lobe (separated by the cruciate fissure) and the occipital lobe. Its primary function is to process skin sensations but it is also associated with spatial body awareness.
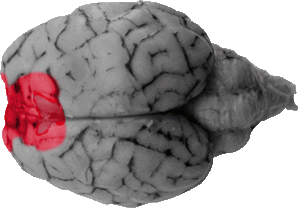
Posterior Lobe of the Cerebellum
The posterior lobe of the cerebellum is the back portion of the vermis. From the dorsal view it is the prominent central feature of the cerebellum.
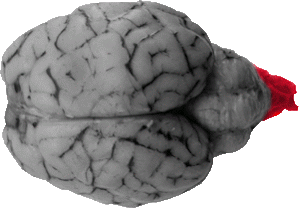
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is the caudal portion of the brain that comes off the back of the cerebellum. This structure is how somatosensory and voluntary motor information can travel between brain and body.
Superior Frontal Gyrus
The superior frontal gyrus runs rostrally from the cruciate fissure and is lateral to the longitudinal fissure.
Superior Frontal Sulcus
The superior frontal sulcus is the line that
comes off the cruciate fissure and is the lateral boundary of the superior frontal gyrus. It also separates this gyrus from the medial frontal gyrus.
Suprasylvian Sulcus
The suprasylvian sulcus is an S-shaped line that generally separates the parietal lobe from the temporal and occipital lobes. It can be seen at the dorso-lateral axis of the brain and can be seen dorsal to the upper extremity of the lateral fissure.
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is laterally separated from the
parietal lobe by the suprasylvian sulcus and this can barely be seen on the dorsal view. Its primary function is to process hearing but has also been associated with emotional behaviors as well as declarative memory retrieval.