PSY3309
Behavioral Neuroscience


Dr. Smith
Florida Southern College
Fornix -Dorsal View
Disclaimer: All structures that have been covered in the lab manual so far can be tagged on a test. This webpage covers the majority of the structures that can be tagged on this view, however, please note that there may be other structures not listed here that can be tagged on the Fornix view.

Anterior Horn of the Lateral Ventricle
The anterior horn of the lateral ventricle will be labeled as the space directly behind the genu of the corpus callosum.This is the very front boundary of the entire lateral ventricle.

Anterior Lobe
The anterior lobe forms a small medial portion of the cerebellum and is separated from the posterior lobe by the fissura prima.

Area Postrema
The very back of the area postrema can be seen behind the cerebellum, where the medulla branches from the spinal chord and forms a "Y". This would also be (if a space)the back of the forth ventricle.

Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is a massive grey protrusion that is bound rosterally by the genu (corpus callosum), medially by the septum pellucidum and fornix, and caudually by the origin of the fimbria. This area is considered to be a major component of the basil ganglia system.

Corpus Cerebelli
The corpus cerebelli comprises the lateral portion of the cerebellum from this view.

Fimbria
The fimbria starts rosterally at the front of the fornix and runs caudo-laterally over the thalamus (not pictured) and in front of the hippocampus. These fibers are extensions of the fornix, and they appear to look like a webbing in front of the hippocampus structure.

Fornix
The fornix is a white strip that runs along the mid-line between the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Towards the genu however, it arches downward, where the septum pellucidum actually connects to the genu.
Fornix Fibers
Fornix fibers are also axon projections of the fornix that completely cover the hippocampus (I.E. the peel of the banana). When labeled, they will be considered white matter.

Genu of the Corpus Callosum
The genu of the corpus callosum is the front of the structure on this view, and it serves as a rostral boundary to the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, the septum pellicidum and the caudate nucleus .
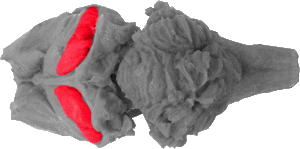
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a banana like structure that wraps around the thalamus (not pictured) down the sides of the brain, following the fimbria. The hippocampus is actually the grey matter inside the structure (I.E. the fruit of the banana), whose white wrapping is called fornix fibers.

Inferior Horn of the Lateral Ventricle
The inferior horn is the very bottom portion of the lateral ventricle, and it can be viewed as the space between the bottom of the hippocampus and the hippocampal gyrus which cannot be see from this view.

Posterior Horn of the Lateral Ventricle
The posterior horn is the space between the back of the hippocampus and the front of the splenium (corpus callosum) it is the very back boundary of each lateral ventricle.

Posterior Lobe
In this view, the posterior lobe comprises most of the medial portion of the cerebellum. It is separated from a small portion of the anterior lobe (via the fissura prima).

Septum Pellucidum
The septum pellucidum is a thin membrane of white matter that is attached to both the genu (corpus callosum) and the fornix. It is the separation of the two lateral ventricles.

Spinal Cord
The spinal cord can be seen at very caudal portion of this view.

Splenium of the Corpus Callosum
The splenium is the very back portion of the corpus callosum, and it forms a large wide "V" that stems from the fornix.