PSY3309
Behavioral Neuroscience


Dr. Smith
Florida Southern College
Sagittal View
Disclaimer: All structures that have been covered in the lab manual so far can be tagged on a test. This webpage covers the majority of the structures that can be tagged on this view, however, please note that there may be other structures not listed here that can be tagged on the sagittal view.
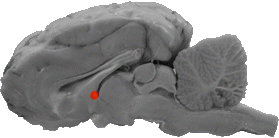
Anterior Commissure
A cross section of the anterior commissure can be seen directly ventrally to the front of the fornix.
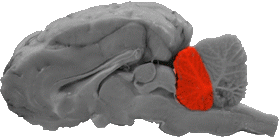
Anterior Lobe
The anterior lobe is the rostral lobe of the cerebellum that is separated from the posterior lobe by the fissura prima.

Anterior Medullary Vellum
The anterior medullary vellum is a thin membrane that separates the cerebral aqueduct from the fourth ventricle.
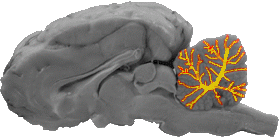
Arbor Vitae
The arbor vitae is a series of axon bundles that allow all lobes of the cerebellum to communicate with each other.

Area Postrema
The area postrema is the dorsal portion of the caudal medulla, and envelopes the beginning of the central canal of the spinal cord.

Basis Pedunculi
The basis pedunculi is the ventral half of the cerebral peduncle.
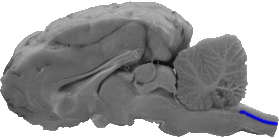
Central Canal of the Spinal Cord
The central canal of the spinal cord is part of the ventricluar system that is contained within the spinal cord.

Cerebellum
From the sagittal view the cerebellum can be divided into an anterior lobe, a posterior lobe, a nodule, and the arbor vitae (the white matter).
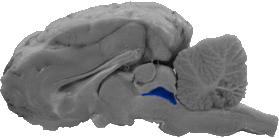
Cerebral Aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (also called the cavity of the midbrain) is part of the ventricular system that flows between the tectum and tegmentum.

Cerebral Peduncle
On a sagittal view, the cerebral peduncle can be divided into an upper half (the tegmentum) and a bottom half (the basis pedunculi).

Cingulate Gyrus
The cingulate gyrus is a cortical area that runs rostrally and dorsally to the corpus callosum.
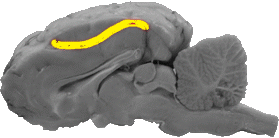
Cingulate Sulcus
The cingulate sulcus is a line that separates the caudal portion of the cingulate gyrus from the parietal lobe.

Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum is a massive bundle of fibers whose cross section can be seen on the sagittal section. It can be divided into four parts: the rostrum, the genu, the main portion, and the splenium.
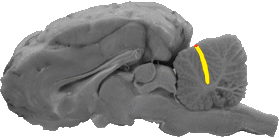
Fissura Prima
The fissura prima is a line that separates the anterior and posterior lobes of the cerebellum.

Fornix
The fornix is a bundle of fibers that arches rostrally over the thalamus.

Fourth Ventricle
The fourth ventricle is part of the ventricular system that lies directly ventral to the cerebellum.

Genu of the Corpus Callosum
The genu is the thick front curvature of the corpus callosum.

Habenular Nucleus
The habenular nucleus is a triangular mass that arises caudally from the top of the thalamus.

Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus serves as the ventral wall on each side of the brain below the thalamus.

Lateral Ventricle
The main part of the lateral ventricle is bounded by the corpus callosum and the fornix.
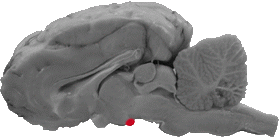
Mammillary Bodies
The mammillary bodies are caudal to the back part of the hypothalamus.

Nodule of the Cerebellum
The nodule is the ventro-caudal lobual of the cerebellum in a sagittal view.
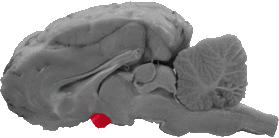
Optic Chiasm
The optic chiasm is rostral to the hypothalamus. A cross section of this structure can be seen on the sagittal view.
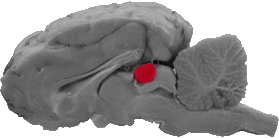
Pineal Body
The pineal body is an oval shaped structure that is caudal to the habenular nucleus, dorsal to the posterior commissure, and rostral to the superior colliculus.

Posterior Commissure
The posterior commissure is a band of fibers that is ventrally connected to the pineal body.
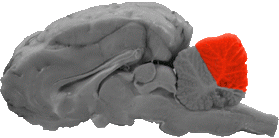
Posterior Lobe of the Cerebellum
The posterior lobe is the dorso-caudal portion of the cerebellum in a sagittal view.
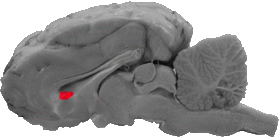
Rostrum of the Corpus Callosum
The rostrum is the small ventral portion (that curves inward) of the corpus callosum.

Septum Pellucidum
The septum pellucidum (if visible) is a membrane on the mid-line that separates the two lateral ventricles.
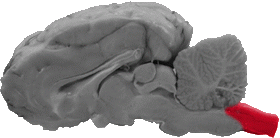
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is the most caudal region of the brain in the sagittal view.
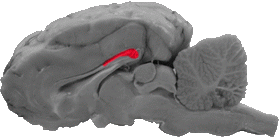
Splenium of the Corpus Callosum
The splenium is the club-shaped caudal portion of the corpus callosum that fuses with the middle of the fornix.
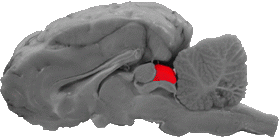
Superior Colliculus
The superior colliculus is caudal to the pineal body, dorsal to the tectum and rostral to the cerebellum.
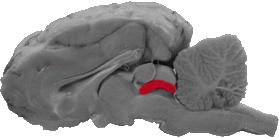
Tectum
The tectum is a white band of fibers that is ventral to the superior colliculus and serves as the roof to the cerebral aqueduct.

Tegmentum
The tegmentum is the dorsal half of the cerebral peduncle.
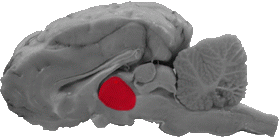
Thalamus
The thalamus is a large rounded mass that is dead center in the brain.

Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is the cavity that completely surrounds the thalamus.