PSY3309
Behavioral Neuroscience


Dr. Smith
Florida Southern College
Lateral View
Disclaimer: All structures that have been covered in the lab manual so far can be tagged on a test. This webpage covers the majority of the structures that can be tagged on this view, however, please note that there may be other structures not listed here that can be tagged on the lateral view.

Anterior Ramus of the Lateral Fissure
The anterior ramus is the branch of the ventral lateral fissure that runs toward the olfactory bulb.

Brachium Pontis
The brachium pontis is the lateral extension of the pons.
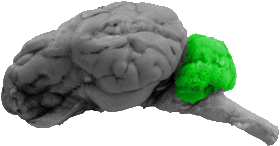
Cerebellum
From the lateral view the following structures can be seen, the posterior lobe, the corpus cerebelli, and the flocculus.

Cerebral Cortex
All lobes of the cerebral cortex can be seen in this view.

Corpus Cerebelli
The corpus cerebelli is the prominent side portion of the cerebellum.
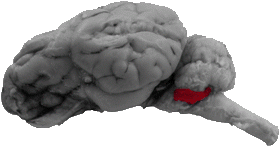
Flocculus
The flocculus is the ventro-lateral lobual that can be seen directly above the brachium pontis, the trigeminal nerve, and the trapezoid body.

Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the rostral one third of the cerebral cortex.

Hippocampal Gyrus
The hippocampal gyrus is the caudal portion of the pyriform lobe and it falls directly below the temporal and occipital lobes.
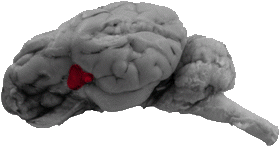
Insula
The insula is bound by all parts of the lateral fissure as well as by the rhinal fissure.

Lateral Fissure
The main portion of the lateral fissure starts on the dorsal portion of the lateral view and goes down the side of the brain, branching into an anterior ramus and a posterior ramus.
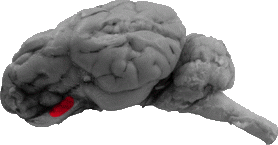
Lateral Olfactory Gyrus
The lateral olfactory gyrus is the area of matter that connects the olfactory bulb to the hippocampal gyrus, and it can be seen directly ventral to the rhinal fissure.

Lateral Olfactory Stria
The lateral olfactory stria is a white stripe that can be seen close to the ventral part of the lateral view. It runs parallel to both the front of the rhinal fissure and the lateral olfactory gyrus.

Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe constitutes the back portion of the cerebral cortex.

Olfactory Bulb
The olfactory bulb can be seen directly below the very front of the rhinal fissure.
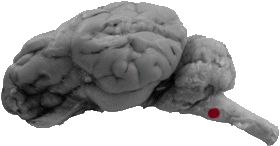
Olive
The olive is directly caudal to the trapezoid body.
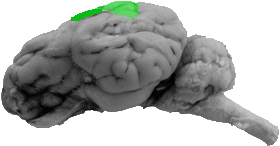
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is the dorsal, middle portion of the cerebral cortex.

Posterior Lobe of the Cerebellum
The posterior lobe constitutes the top medial portion of the cerebellum.
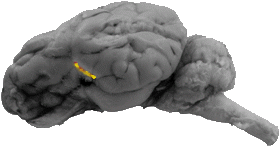
Posterior Ramus of the Lateral Fissure
The posterior ramus runs to the back of the insula at the ventral part of the lateral fissure.

Pyramid
The pyramid is the ventral part of the medulla.

Pyriform Lobe
The pyriform lobe consists of the lateral olfactory gyrus (rostrally) and the hippocampal gyrus (caudally).
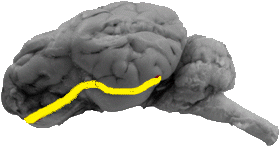
Rhinal Fissure
The rhinal fissure separates the cerebral cortex from the pyriform lobe.
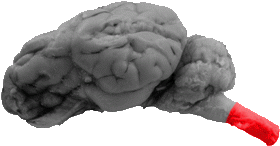
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord serves as the caudal portion of this view.
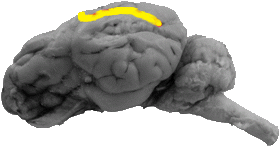
Suprasylvian Sulcus
The suprasylvian sulcus is the line that separates the parietal lobe from the temporal lobe and it can be seen on the dorsal portion of this lateral view.
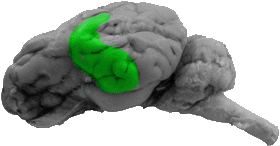
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe constitutes most of the side portion of the cerebral cortex.