PSY3309
Behavioral Neuroscience


Dr. Smith
Florida Southern College
Horizontal - Upper View
Disclaimer: All structures that have been covered in the lab manual so far can be tagged on a test. This webpage covers the majority of the structures that can be tagged on this view, however, please note that there may be other structures not listed here that can be tagged on the horizontal view.
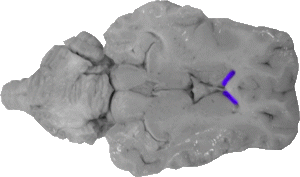
Anterior Horn of the Lateral Ventricle
The anterior horns of the lateral ventricle are the spaces directly behind the genu of the corpus callosum, and they mark the front boundary of the lateral ventricles.
Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule
The anterior limb of the internal capsule marks the front portion of the structure, and this part of the internal capsule runs along the entire caudate nucleus.
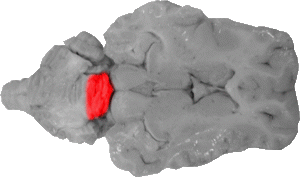
Anterior Lobe of the Cerebellum
The anterior lobe comprises the front one third of the central cerebellum and is separated from the posterior lobe by the fissura prima.
Arbor Vitae
The arbor vitae are the white fibers that run throughout the section of the cerebellum.
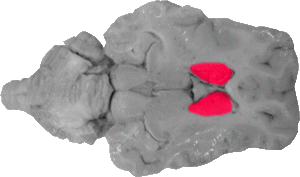
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nuclei are large grey masses that fall lateral to the septum pellucidum and fornix. They mark the medial portion of the basal ganglia system.
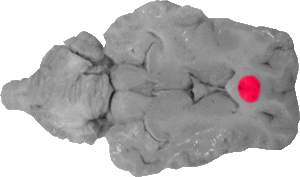
Cingulate Gyrus
The cingulate gyrus is the cortex directly rostral to the genu of the corpus callosum on this view.

Claustrum
The claustrum is the grey area that lies between the external and extreme capsules.
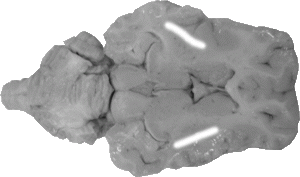
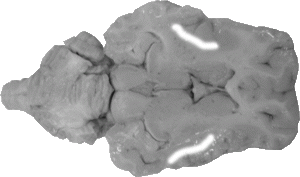
Extreme Capsule
The extreme capsule is a scallop-shaped line that separates the claustrum from the insula.
Fimbria
The fimbria is a white pointed tip that is directly rostral to the hippocampus.

Fissura Prima
The fissura prima is the line the separates the anterior and posterior lobes of the cerebellum.
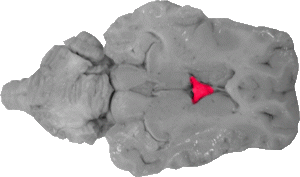
Fornix
The fornix is a triangular fiber bundle that lies between the thalamus and the septum pellucidum.

Genu of the Corpus Callosum
The genu of the corpus callosum is a "V" shaped bundle of fibers whose point is directly rostral to the septum pellucidum.
Genu of the Internal Capsule
The genu of the internal capsule marks the bend of the structure between its anterior and posterior limbs.

Habenular Nucleus
The habenular nuclei appear to be two white circles that are directly rostral to the pineal gland and serve as medio-caudal boundaries to the thalamus.

Hippocampus
The hippocampus is the grey matter that appears lateral to the superior colliculus and caudo-lateral to the back of the thalamus.
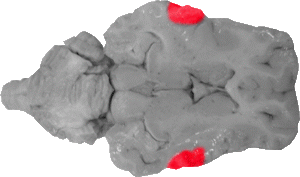
Insula
The insula marks the lateral boundary of the entire basal ganglia system and is lateral to the extreme capsule.

Lentiform Nucleus
The lentiform nuclues comprises of both the putamen and globus pallidus nuclei of the basal ganglia system, and it can be seen as the grey area that is lateral to the entire internal capsule and medial to the external capsule.
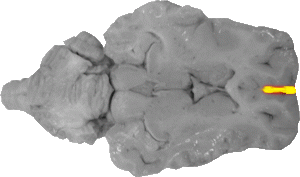
Longitudinal Fissure
The longitudinal fissure is the line that runs medially through the cortex in the front of this view.
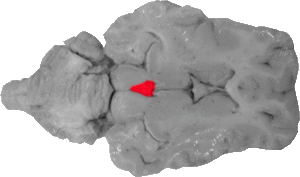
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland is a mass that is wedged between the front portions of the superior colliculi.
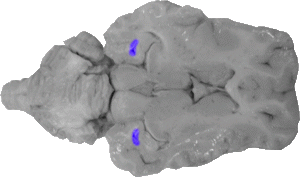
Posterior Horn of the Lateral Ventricle
The posterior horn of the lateral ventricle are the spaces that fall directly behind the hippocampus on an upper horizontal view.

Posterior Limb of the Internal Capsule
The posterior limb marks the caudal portion of the internal capsule that deviates to the side of the emerging thalamus.
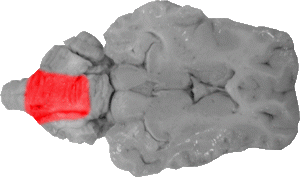
Posterior Lobe of the Cerebellum
The posterior lobe of the cerebellum comprises two thirds of the central cerebellum and is separated from the anterior lobe via the fissura prima.
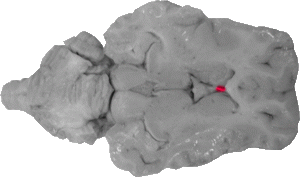
Septum Pellucidum
The septum pellucidum is a thin membrane that connects the fornix with the genu of the corpus callosum. It helps separate the two lateral ventricles.
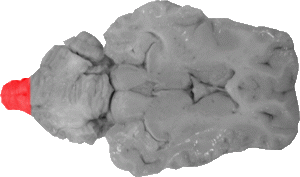
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord marks the very caudal portion of the section.

Superior Colliculus
The superior colliculi are two touching rounded masses that are directly rostral to the cerebellum. This constitutes the midbrain on this view.

Thalamus
The thalamus arises past the fornix and extends to the front of the habenular nuclei, the superior colliculi, and the hippocampi/fimbriae.
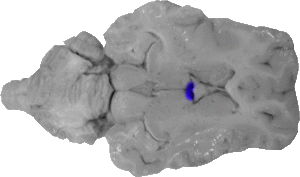
Third Ventricle
In this view, the third ventricle is the space between the fornix and the front of the thalamus.